Dental stents Implants
 Journal:Guided Dental Implant Surgery Volume: vol. 8 No. 2
Journal:Guided Dental Implant Surgery Volume: vol. 8 No. 2
Authors:Heba E. Khorshid, Hamdy Aboul Fotouh Hamed, Essam A. Aziz, Dr. Les Kalman, Kyung-ah Jang, Nelson G. Woo, Paul D. Eleazer, Michael D. Huffer, Souheil Hussaini, Elham Yagoobi, Maryam Khalili, Saul Weiner
11. The Effect of CAD/CAM versus Conventional Casting Frameworks on the Passivity of Fit for Screw Retained Implant Supported Maxillary Prostheses
The Target of this work was to study the effect of two different techniques of framework construction; Conventional Cast Metal Technology and the CAD/CAM Technology on the passivity of fit of screw-retained prostheses placed in the completely edentulous maxillae. CAD/CAM restorations yielded a more favourable bone reaction at the bone/ implant interface than the Conventional Casting group thus should be considered as a viable alternative to cast restorations for implant frameworks.
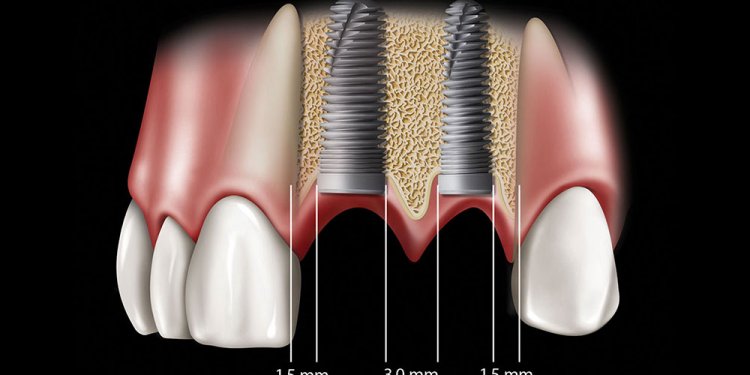
23. Revisiting a Modified Chair-Side Radiographic and Surgical Stent for Template-Assisted Surgery: A Case Report
The prosthodontic driven implant has become the standard in dentistry. Prosthesis location should dictate the implant site in diagnosis, treatment planning and surgery in implantology. Although there are several methods to achieve a prosthodontically-driven result, through guided and assisted surgery, there can be various barriers to the technology. The ability to custom build the stent allows the clinician to have control of his/ her implant surgery by determining implant position and angulation. The RS stent is inexpensive, accessible and provides immediate fabrication.
31. Exothermic Reaction Temperatures of Various Volumes of Calcium Sulfate Bone Graft Material
Root-end resection can create bony crypts needing grafting. Anecdotal reports indicate calcium sulfate may fail because of exothermic reactions. The purpose of this study was to evaluate setting heat from 3 mm diameter x 7 mm deep and larger volumes. The alpha hemihydrate form of calcium sulfate is not exothermic during setting.
39. The Effects of Professional Based Education upon the Interest of a Disadvantaged Population in Implant-Related Treatment
The purpose of this project was to report the value of a strategy to motivate a disadvantaged population, limited in their opportunities for information, regarding dental and oral care with specific reference to dental implants. Instruction by a dentist significantly improved the interest of a population with limited education background and poor socioeconomic class in replacement of missing dentition with an implant.