Worldwide Dental Services
- Worldwide, 60–90% of school children and nearly 100% of adults have dental cavities.
- Dental cavities can be prevented by maintaining a constant low level of fluoride in the oral cavity.
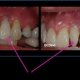
- Severe periodontal (gum) disease, which may result in tooth loss, is found in 15–20% of middle-aged (35-44 years) adults.
- Globally, about 30% of people aged 65–74 have no natural teeth.
- Oral disease in children and adults is higher among poor and disadvantaged population groups.
- Risk factors for oral diseases include an unhealthy diet, tobacco use, harmful alcohol use and poor oral hygiene, and social determinants.
Oral health is essential to general health and quality of life. It is a state of being free from mouth and facial pain, oral and throat cancer, oral infection and sores, periodontal (gum) disease, tooth decay, tooth loss, and other diseases and disorders that limit an individual’s capacity in biting, chewing, smiling, speaking, and psychosocial wellbeing.
Oral diseases and conditions
The most common oral diseases are dental cavities, periodontal (gum) disease, oral cancer, oral infectious diseases, trauma from injuries, and hereditary lesions.
Dental cavities
Worldwide, 60–90% of school children and nearly 100% of adults have dental cavities, often leading to pain and discomfort.
Periodontal disease
Severe periodontal (gum) disease, which may result in tooth loss, is found in 15–20% of middle-aged (35-44 years) adults.
Tooth loss
Dental cavities and periodontal disease are major causes of tooth loss. Complete loss of natural teeth is widespread and particularly affects older people. Globally, about 30% of people aged 65–74 have no natural teeth.
Oral cancer
The incidence of oral cancer ranges from one to 10 cases per 100 000 people in most countries. The prevalence of oral cancer is relatively higher in men, in older people, and among people of low education and low income. Tobacco and alcohol are major causal factors.
Fungal, bacterial or viral infections in HIV
Almost half (40–50%) of people who are HIV-positive have oral fungal, bacterial or viral infections. These often occur early in the course of HIV infection.
Oro-dental trauma
Across the world, 16-40% of children in the age range 6 to12 years old are affected by dental trauma due to unsafe playgrounds, unsafe schools, road accidents, or violence.
Noma
Noma is a gangrenous lesion that affects young children living in extreme poverty primarily in Africa and Asia. Lesions are severe gingival disease followed by necrosis (premature death of cells in living tissue) of lips and chin. Many children affected by noma suffer from other infections such as measles and HIV. Without any treatment, about 90% of these children die.
Cleft lip and palate
Birth defects such as cleft lip and palate occur in about one per 500–700 of all births. This rate varies substantially across different ethnic groups and geographical areas.
Common causes
Risk factors for oral diseases include an unhealthy diet, tobacco use and harmful alcohol use. These are also risk factors for the four leading chronic diseases – cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes – and oral diseases are often linked to chronic disease. Poor oral hygiene is also a risk factor for oral disease.